Dichroic.Asia Optical
HOME > Info > About coating
 About Coating
About Coating
How to change the transparent colorless glass to achieve the desired spectrum or color, but also to maintain or even improve the penetration rate, and need not fade or peel off, the method is to apply a film on the glass.
The thickness of a single layer film is generally tens to thousands of angstroms (A = 10 -7 mm), because the general bulk material is made into such a thin type. State, special methods must be used.
At present, optical film production is mainly based on physical evaporation, which is carried out by converting the film material from a solid state to a gaseous state or an ionic state. A gaseous or ionic material that passes through the space from the evaporation source and reaches the glass surface. After the material reaches the surface of the glass, it will deposit and gradually form a film.
Because the film is made to have high purity, the coating process is completed in a high vacuum environment.
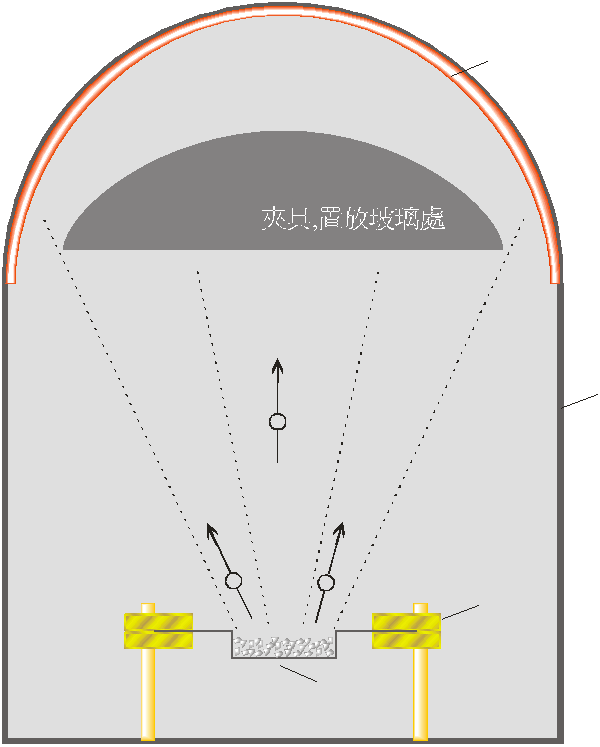
The actual working process of optical coating is simplified as follows: the substrate is washed with an ultrasonic cleaner, washed, placed on a jig, fed into a coater, and heated and vacuumed. After the high vacuum is reached, the coating is started.
When the coating process is carried out, the coating material is changed to an ionic state by electron gun or resistive heating. Since the coating machine is in a high vacuum state, the ionic coating material can smoothly reach the substrate. Generally, the multilayer film is matched with a high refractive material and a low refractive material. Common high refractive materials such as titanium oxide (TiO2, Ti3O5) or tantalum oxide (Ta2O5), low refractive materials such as lanthanum oxide (SiO2) or magnesium fluoride (MgF2), sometimes with medium refractive materials such as alumina (Al2O3) or zirconia (ZrO2).
The coating time varies depending on the number of layers and the program, ranging from tens of minutes to several hours. After the coating is completed, remove it after the temperature has cooled. The coated glass, collectively referred to as an optical interference filter, has the function of interfering with light and filtering certain wavelengths.
According to the characteristics of the filter, it can be subdivided into AR coating or AR coating, IR Cut or Hot Mirror, and infrared penetration ( IR Pass) or Cold Mirror, UV Cut, Band Pass or narrow band filters, Long Pass, Short Pass filters, and more.